Google has, very helpfully, issued a Search Engine Optimization Starter Guide. This is a more detailed version of the content of their excellent online training course the digital garage.
The information was originally intended for internal consumption in Google; however it has made the document publicly available to help Webmasters and website owners improve their websites.
Although they are at pains to stress that there are no shortcuts and secrets, they stress a key objective is making it easier for search engines to crawl, index and understand your content.
This often entails making many small improvements to your website which combine to result in improvements to the site’s user experience and performance in organic search results.
Here are the main areas covered by the guide.
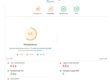
Create accurate Page Titles
The page title tag appears as the blue, bolded, underlined text on a Google search results page, and also on the top left the browser bar. The title tag informs both users and search engines the topic of a particular page.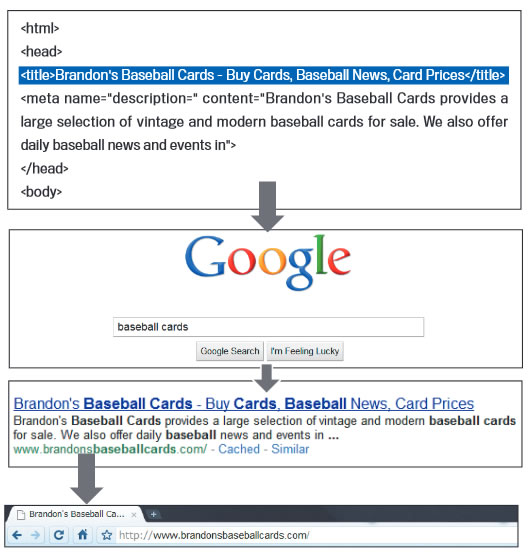
The page title for your homepage can list the name of your website or business and could include other bits of important information like the physical location of the business or maybe a few of its main focuses or offerings.
Here are some other good practice tips:
- Accurately describe the page’s content – Choose a title that effectively communicates the topic of the page’s content.
- Create unique title tags for each page – This shows Google how a page is different from other pages.
- Use brief, but descriptive titles – Titles can be both short and informative. If the title is too long, Google will show only a portion of it in the search result. The current limit is 70 characters.
Make use of the “description” meta tag
The meta description appears on a Google search results page under the page title. The meta description helps people decide whether to click on your result, or a result above or below you. Therefore it needs to attract interest and be compelling as a call to action. Here are some other good practice tips:
Here are some other good practice tips:
- Accurately summarize the page’s content – Write a description that would both inform and interest users if they saw your description meta tag as a snippet in a search result.
- Use unique descriptions for each page – if your site has thousands of pages then you might need your CMS to generate this content automatically.
Use readable URLs
The website page’s URL should include the primary keyword. Each word in the URL should be separated using dashes.
Best practice tips:
- Use words in URLs – URLs with words that are relevant to your site’s content and structure are friendlier for visitors navigating your site.
- Create a simple directory structure – Use a directory structure that organizes your content well and makes it easy for visitors to know where they’re at on your site.
- Provide one version of a URL to reach a document – focus on using and referring to one URL in the structure and internal linking of your pages. You may also use canonical URL or use the rel=”canonical” link element if you can’t redirect.
Make your site easier to navigate
Navigation is a very important part of your website for both users and search engines.
For users it helps them find what they want. For search engines it’s a way of figuring out which pages are most important and provide further clues on the content of the website.
- Plan out your navigation based on your homepage – Unless your site has only a handful of pages, you should think about how visitors will go from your homepage to a page containing more specific content.
- Ensure more convenience for users by using ‘breadcrumb lists’ – A breadcrumb is a row of internal links at the top or bottom of the page that allows visitors to quickly navigate back to a previous section or the root page.
- Prepare two sitemaps: one for users, one for search engines – create a linked text sitemap, plus an XML sitemap which is submitted to Google through the Google Search Console.
Offer quality content and services
Create compelling content that users will likely want to direct other users. This could be through blog posts, social media services, email, forums, or other means.
Organic or word-of-mouth buzz is what helps build your site’s reputation with both users and Google, and it rarely comes without quality content.
Best practice tips:
- Make your content relevant with keyword research – use premium or free tools such as Google Keyword tool to discover what searches are being made on Google with volumes and suggestions.
- Write easy to read text – maintain good standards of spelling and grammar.
- Create fresh, unique content – New content will not only keep your existing visitor base coming back, but also bring in new visitors.
- Make internal links – paying more attention to the anchor text used for internal links can help users and Google navigate your site better.
- Use descriptive anchor text – anchor text you use for a link should provide at least a basic idea of what the page linked to is about. Avoid anchor text like click here.
Optimise your images
All images can have a distinct filename and “alt” attribute, both of which you should make relevant to the content. This helps search engines understand your content as well as those who need to use screen readers.
Avoid using generic filenames like “image1.jpg”, “pic.gif”, “1.jpg” when possible—some sites with thousands of images might consider automating the naming of images. Also avoid going the other way and using overlong or keyword stuffed filenames.
Use heading tags properly
Not to be confused with unseen meta tags, these are the HTML tags that create headings within the page. There are six sizes of heading tags, beginning with <h1>, the most important, and ending with <h6>, the least important.
Multiple heading sizes are used in order create a hierarchical structure for your content, making it easier for users to navigate through your document.
Best practice tips:
- Use headings naturally – however bear in mind that Google will pay attention to the text of headings to understand the page contents.
- Don’t always use headings – other tags like <em> and <strong> may be more appropriate.
- Use one H1 tag and as many as you want of other tags – make sure it’s consistent and the page looks right.
Make your website mobile friendly
Having a mobile ready site is critical to your online presence. In fact, starting in late 2016, Google has begun experiments to primarily use the mobile version of a site’s content for ranking, parsing structured data, and generating snippets.
This is called mobile-first indexing and is now being rolled out across the web.
If your site serves lots of static content (like blog posts or product landing pages) across multiple pages, consider implementing it using AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages). It’s a special flavour of HTML that ensures your site stays fast and user friendly, and can be further accelerated by various platforms, including Google Search.
Promote your website
Effectively promoting your new content will lead to faster discovery by those who are interested in the same subject. As with most points covered in this document, taking these recommendations to an extreme could actually harm the reputation of your site.
Putting effort into the offline promotion of your company or site can also be rewarding. Make sure your URL is on letterheads and business cards
If you run a local business, adding its information to Google My Business will help you reach customers on Google Maps and web search.
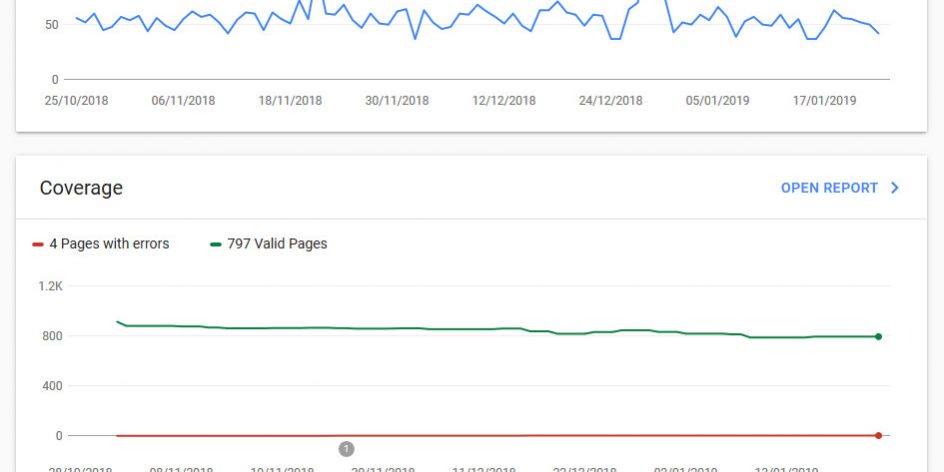
Analyse your website data
Add Google analytics to your website and it will give you a vast amount of information about how users interact with your website:
- Discover the most popular content on your site
- Measure the impact of optimizations you make to your site
Google Search Console gives you insight on the following:
- Can Google find my content?
- How is my website performing in Google Search results?
Using Search Console won’t help your site get preferential treatment; however, it can help you identify issues that, if addressed, can help your site perform better in search results.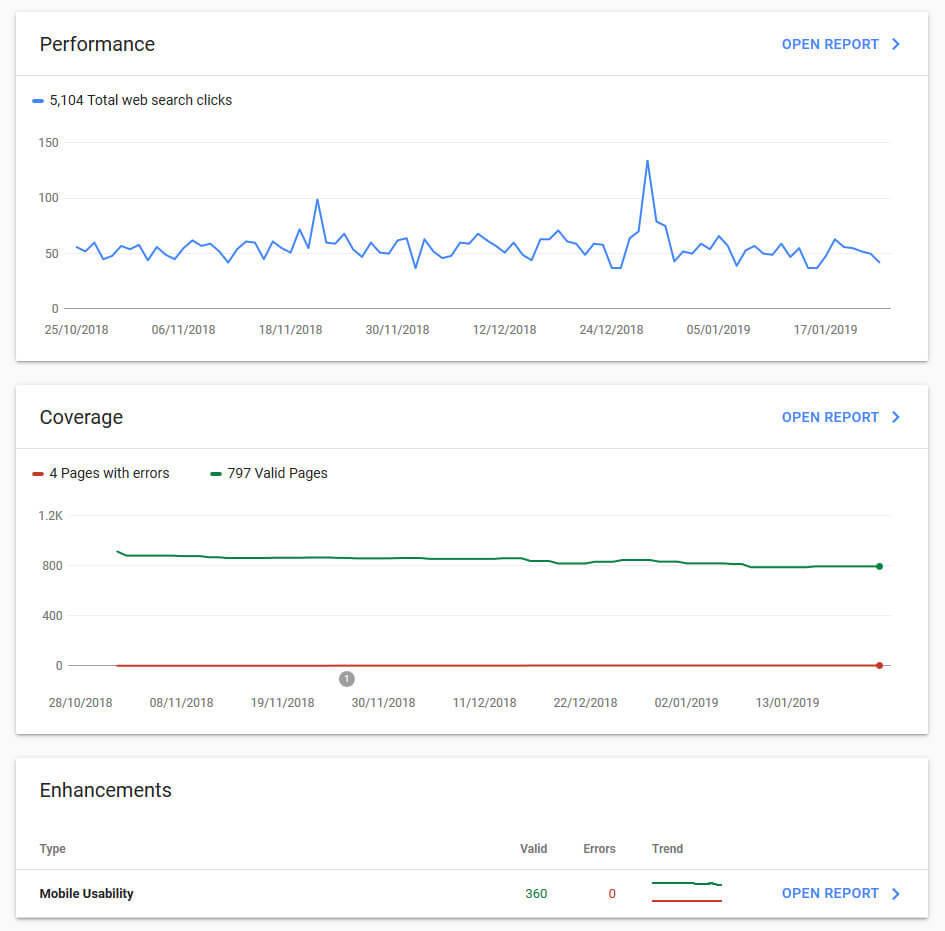
Other more specialist tools can reveal the following:
- Mobile Friendly test
- Website speed
- Backlinks
- Ranking on search engines
- Technical audit data such as broken links
Gather all the information you can about your website and act on the facts.
There is much more information at the guide page here: https://support.google.com/webmasters/answer/7451184?hl=en
The information is generally very useful however omits contentious issues like link building and outreach where Google would prefer website owners to focus on building an excellent, user-focused website.
Get in touch with Dinesh on 07941 686113 if you need help on web design Rugby, web hosting, SEO services, domain names or email marketing.
Further reading
How to Become an SEO Expert: A Guide to FREE Online SEO Training